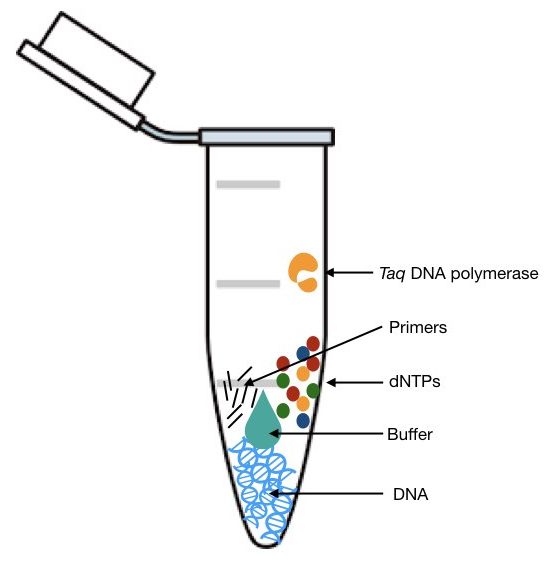
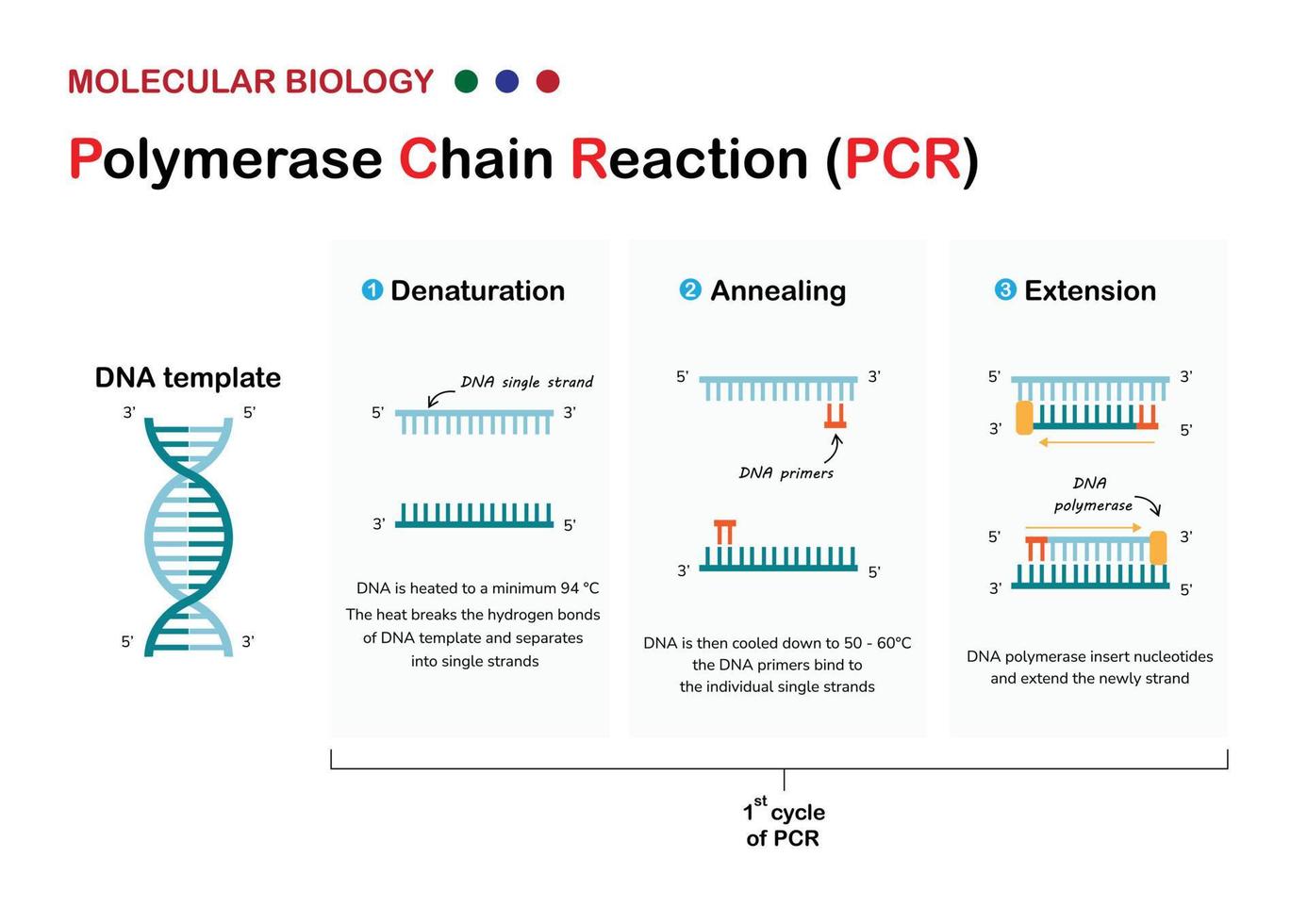
Understanding the role of DNA polymerase in PCR function is crucial for anyone involved in molecular biology research. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a groundbreaking technique used to amplify DNA sequences, and DNA polymerase plays an indispensable role in this process. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms of DNA polymerase, its importance in PCR, and how it has revolutionized scientific research.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) has become an essential tool in modern biology, enabling scientists to replicate DNA sequences with remarkable precision. At the heart of this process lies DNA polymerase, an enzyme that facilitates the synthesis of new DNA strands. This article will explore the function of DNA polymerase in PCR, its variations, and the impact it has had on scientific advancements.
As we unravel the complexities of DNA polymerase in PCR function, we will also examine its applications in various fields, from medical diagnostics to forensic science. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of DNA polymerase in PCR and its pivotal role in modern biotechnology.
Read also:Vegamovies Anime Hindi Dubbed Download Your Ultimate Guide
What is DNA Polymerase?
DNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during DNA replication. It plays a critical role in maintaining genetic information by adding nucleotides to the growing DNA chain, ensuring the fidelity of genetic material.
DNA polymerase operates by recognizing the template strand of DNA and pairing complementary nucleotides to it. This process ensures that the genetic information is accurately copied during cell division. There are several types of DNA polymerases, each with specific functions and characteristics.
Types of DNA Polymerase
- DNA Polymerase I: Primarily involved in the repair of DNA and removal of RNA primers during replication.
- DNA Polymerase II: Plays a role in repairing damaged DNA strands.
- DNA Polymerase III: The primary enzyme responsible for DNA replication in prokaryotes.
- Taq Polymerase: A thermostable enzyme commonly used in PCR due to its ability to withstand high temperatures.
Each type of DNA polymerase has unique properties that make it suitable for specific biological processes, including PCR.
Understanding Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It allows scientists to produce millions of copies of a target DNA sequence in a short amount of time, making it an invaluable tool in genetic research.
Steps in the PCR Process
- Denaturation: The double-stranded DNA is heated to separate it into two single strands.
- Annealing: Primers bind to the target DNA sequence at a lower temperature.
- Extension: DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides.
These steps are repeated in cycles, exponentially increasing the number of DNA copies. The efficiency of PCR depends heavily on the quality and stability of the DNA polymerase used.
The Role of DNA Polymerase in PCR Function
In PCR, DNA polymerase is responsible for extending the DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the primer-template junction. Its thermostability and ability to function at high temperatures make it ideal for this process.
Read also:Unveiling The Journey Of Barbara Ann Bregoli From Fame To Fortune
Key Characteristics of DNA Polymerase in PCR
- Thermostability: DNA polymerases used in PCR, such as Taq polymerase, can withstand the high temperatures required for denaturation.
- Fidelity: High-fidelity polymerases ensure accurate replication of DNA sequences, minimizing errors.
- Efficiency: The speed and efficiency of DNA polymerase directly impact the success of PCR amplification.
These characteristics are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of PCR results.
Variations of DNA Polymerase for PCR
Several variations of DNA polymerase have been developed to meet the diverse needs of PCR applications. These variations offer improved thermostability, fidelity, and efficiency, making them suitable for different experimental conditions.
Popular DNA Polymerases Used in PCR
- Taq Polymerase: Widely used for standard PCR due to its thermostability and cost-effectiveness.
- Pfu Polymerase: Known for its high fidelity, making it ideal for applications requiring accurate DNA replication.
- Phusion Polymerase: Combines high fidelity and speed, suitable for complex PCR applications.
Choosing the right DNA polymerase depends on the specific requirements of the experiment, such as the length of the DNA sequence and the desired level of accuracy.
Applications of DNA Polymerase in PCR
DNA polymerase in PCR has a wide range of applications across various fields, including medical diagnostics, forensic science, and genetic engineering.
Medical Diagnostics
In medical diagnostics, PCR is used to detect genetic mutations and infectious diseases. DNA polymerase ensures the accurate amplification of target DNA sequences, enabling precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
Forensic Science
Forensic scientists rely on PCR to analyze DNA samples from crime scenes. DNA polymerase facilitates the amplification of minute DNA samples, providing critical evidence in criminal investigations.
Genetic Engineering
PCR is a fundamental tool in genetic engineering, allowing scientists to manipulate DNA sequences for research and development purposes. DNA polymerase plays a crucial role in this process, ensuring the fidelity and efficiency of DNA replication.
Advancements in DNA Polymerase Technology
Recent advancements in DNA polymerase technology have significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of PCR. Researchers continue to develop new polymerases with enhanced properties, expanding the possibilities of molecular biology.
Engineered DNA Polymerases
Engineered DNA polymerases are designed to overcome the limitations of naturally occurring enzymes. These polymerases offer improved thermostability, fidelity, and processivity, making them suitable for challenging PCR applications.
Next-Generation PCR Techniques
Next-generation PCR techniques, such as digital PCR and real-time PCR, rely on advanced DNA polymerases to provide highly sensitive and accurate results. These techniques have revolutionized the field of molecular biology, enabling researchers to study complex biological systems with unprecedented precision.
Challenges and Limitations of DNA Polymerase in PCR
Despite its advantages, DNA polymerase in PCR is not without limitations. Factors such as enzyme fidelity, amplification bias, and contamination can affect the accuracy and reliability of PCR results.
Factors Affecting PCR Efficiency
- Enzyme Fidelity: Errors during DNA replication can lead to inaccurate results, necessitating the use of high-fidelity polymerases.
- Amplification Bias: Unequal amplification of DNA sequences can skew results, requiring careful optimization of PCR conditions.
- Contamination: Cross-contamination of DNA samples can compromise the integrity of PCR results, emphasizing the importance of stringent laboratory protocols.
Addressing these challenges requires a thorough understanding of DNA polymerase properties and careful optimization of PCR conditions.
Future Directions in DNA Polymerase Research
Ongoing research in DNA polymerase is focused on developing enzymes with enhanced properties, such as higher fidelity, thermostability, and processivity. These advancements will further expand the capabilities of PCR, enabling new applications in molecular biology.
Potential Applications of Advanced DNA Polymerases
- Personalized Medicine: Advanced DNA polymerases could enable more accurate genetic testing, paving the way for personalized treatment plans.
- Synthetic Biology: Engineered DNA polymerases may facilitate the creation of synthetic organisms with novel capabilities.
- Environmental Monitoring: PCR techniques using advanced polymerases could enhance the detection of environmental contaminants and pathogens.
As research in this field progresses, the potential applications of DNA polymerase in PCR are virtually limitless.
Conclusion
DNA polymerase plays a vital role in PCR function, enabling the accurate and efficient amplification of DNA sequences. Its thermostability, fidelity, and efficiency make it an indispensable tool in molecular biology research. From medical diagnostics to forensic science, the applications of DNA polymerase in PCR are diverse and far-reaching.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with DNA polymerase in PCR in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the fascinating world of molecular biology.
Table of Contents
- What is DNA Polymerase?
- Understanding Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- The Role of DNA Polymerase in PCR Function
- Variations of DNA Polymerase for PCR
- Applications of DNA Polymerase in PCR
- Advancements in DNA Polymerase Technology
- Challenges and Limitations of DNA Polymerase in PCR
- Future Directions in DNA Polymerase Research
- Conclusion